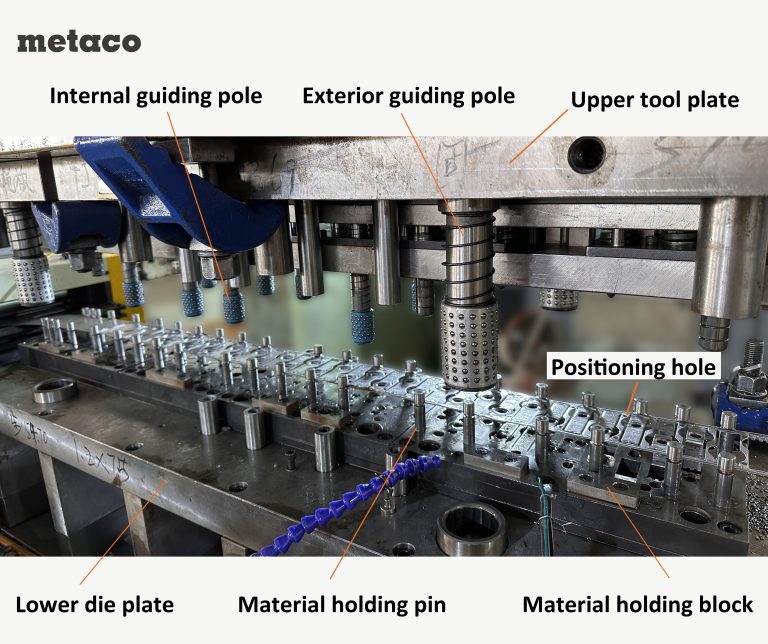
Common Defects in Metal Stamping Process and Their Causes
Table of Contents
1. Cracking and Fractures
Cause: This defect occurs when the material is subjected to excessive stress during the forming process, often due to improper die design, excessive forming force, or insufficient material ductility. Cracking can also result from high internal stresses or poor material quality.
Solution: Adjust die design to reduce stress concentration, select materials with better ductility, and optimize process parameters such as forming force and speed.

2. Burr Formation
Cause: Burrs are small, unwanted projections of material along the edges of the stamped part. They typically form when the cutting edges of the die do not provide a clean separation, often due to worn-out or dull cutting edges, improper clearance between die and punch, or incorrect material thickness.
Solution: Regular maintenance of dies, correct clearance settings, and material pre-treatment (e.g., lubrication) can help reduce burr formation.

3. Denting
Cause: Dents or dimples appear when the material is improperly supported or the die lacks sufficient rigidity. It can also occur due to excessive forming force, which deforms the material in unintended locations.
Solution: Ensure proper die and material alignment, adjust forming forces, and use adequate support fixtures to prevent deformation.
4. Wrinkling
Cause: Wrinkling occurs when there is uneven material flow during the stamping process, often caused by insufficient material draw or improper die design. It can also occur if the material is too thin or if the punch and die do not apply uniform pressure.
Solution: Proper die design to control material flow, optimized blank holder force, and ensuring appropriate material thickness can help eliminate wrinkling.

5. Excessive Springback
Cause: Springback is the elastic recovery of the material after the forming process. It typically happens when the material is over-stressed or the die’s bend radius is too small. It leads to dimensional inaccuracy, especially in parts with bends or angles.
Solution: Use pre-stretching techniques, adjust the die radius, and apply compensations in the die design to account for material recovery.

6. Uneven Thickness
Cause: Thickness variation in stamped parts may occur due to non-uniform pressure distribution or uneven material flow during the forming process. It is also common in parts with complex shapes or deep draws.
Solution: Optimize die design to improve pressure distribution, use more gradual forming techniques, and ensure proper material feeding.

7. Inconsistent Surface Finish
Cause: Poor surface finish is typically caused by improper lubrication, wear on the die surfaces, or contamination between the die and material. It can also be due to incorrect press speed or temperature during the forming process.
Solution: Use adequate lubrication, ensure clean die surfaces, and adjust the press speed and temperature to suit the material being formed.

8. Dimensional Inaccuracy
Cause: Parts may not meet dimensional specifications due to incorrect die clearance, improper press alignment, or fluctuations in material properties.
Solution: Regular die maintenance, accurate press setup, and ensuring material consistency can minimize dimensional inaccuracy.
9. Material Flow Issues
Cause: Material flow issues can occur when the material doesn’t move evenly into the die cavity, often due to insufficient draw or improper die geometry.
Solution: Ensure proper die design to support uniform material flow and consider adding features like draw beads or controlling blank holder pressure.