Precision Metal Stamping and Rapid Prototyping
Rapid Prototyping (RP) is a process that uses rapid forming technology to quickly produce product prototypes, aimed at accelerating product design and validation. During the rapid prototyping phase, traditional mold making may require a long time and incur high costs. However, the combination of precision metal stamping and rapid prototyping technology can help design teams quickly produce metal samples for design validation, thus optimizing the production process.
Table of Contents
Advantages of Precision Metal Stamping and Rapid Prototyping
1. Shortening the Development Cycle
Traditional mold making typically requires weeks or even longer. Through rapid prototyping, samples can be produced in just a few days. After combining with precision metal stamping, design teams can quickly validate designs and reduce development time.
2. Cost Reduction
During the rapid prototyping phase, there is no need for the high cost of traditional molds. By using precision metal stamping and rapid prototyping, metal samples can be produced using simple molds or 3D printed molds, reducing the cost of trial production.
3. Improving Design Accuracy
Precision metal stamping itself provides high accuracy. Therefore, prototypes made using precision metal stamping can closely meet the final product’s design requirements, reducing issues caused by design errors.
4. Optimizing the Production Process
By combining precision metal stamping with rapid prototyping, design teams can quickly validate designs in a short time and optimize designs based on feedback from the prototypes. This helps improve the subsequent production process.
5. Suitable for Small-Batch Production
Traditional metal stamping molds are suited for large-scale production, while the combination of rapid prototyping and precision metal stamping can effectively meet the needs of small-batch and customized production.
Challenges in Rapid Prototyping and Solutions
1. Material Selection Limitations
The material selection for rapid prototyping is sometimes limited, especially when using technologies like 3D printing. The printed metal molds may not be as durable as traditional molds. The solution is to choose materials suitable for rapid prototyping and ensure the final quality of the prototype parts through precision metal stamping.
2. Precision and Tolerance Control
Although rapid prototyping can quickly generate samples, its precision is often not as good as traditional manufacturing processes. By using precision metal stamping, prototypes can be made to meet the design requirements while ensuring high accuracy.
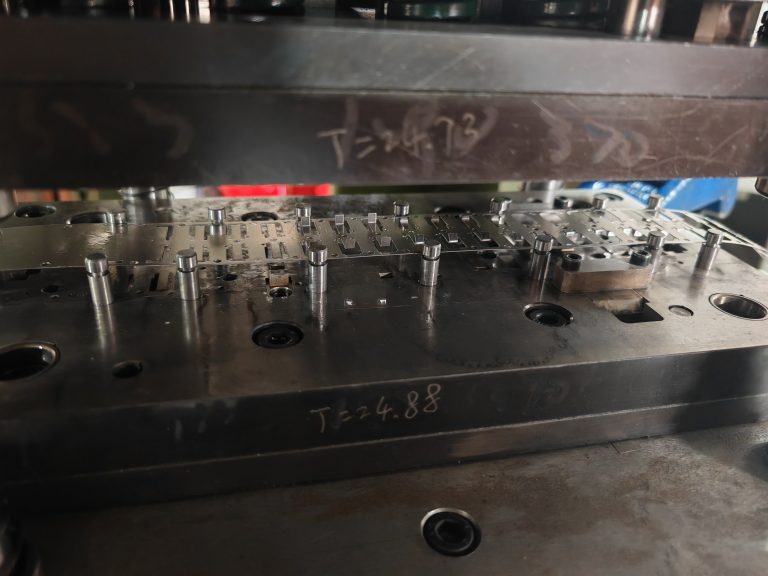
3. Mold Design
Rapid prototyping often relies on simple mold designs, which may not meet the precision stamping requirements. To address this issue, design teams can use advanced mold design technologies, such as 3D printing, to create molds that meet the required standards and ensure the quality of the prototype parts.