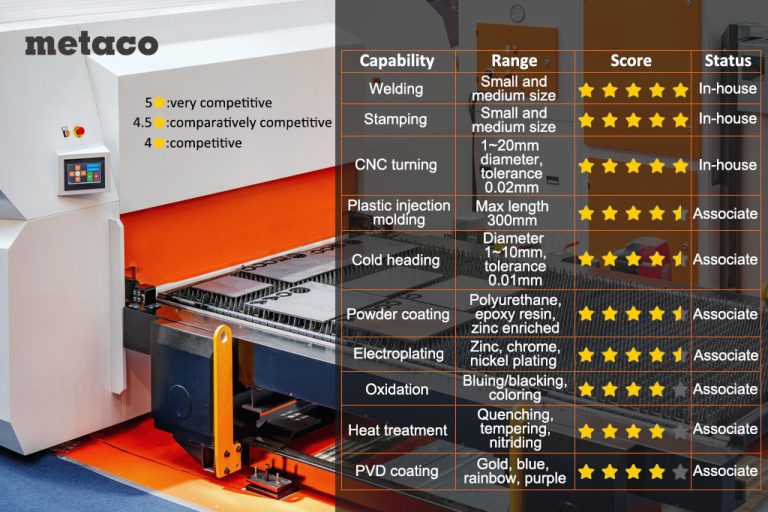
Common Welding Problems and Solutions
Welding is a complex process, and various problems are often encountered during actual operations. Metaco will introduce some common welding problems and provide simple and easy-to-understand solutions.
Table of Contents
1. Porosity
Porosity refers to small holes in the weld, which are usually caused by air or gas being trapped in the welding material during the welding process. These pores may affect the strength of the weld.
Solution: Keep the welding rods dry, slightly increase the current, and avoid welding in damp environments.
2. Cracks
Welding cracks are fissures that form during the welding process, typically on the material surface or within the weld. Cracks can weaken the weld strength and even lead to structural failure.
Solution:
3. Lack of Fusion
Lack of fusion occurs when the weld does not completely integrate with the material, resulting in a weak connection. This usually happens when the material is too thick.
Solution: Maintain a steady speed: Ensure the welding speed is neither too fast nor too slow to maintain consistency.
4. Burnthrough
Burnthrough occurs when excessive heat causes the material to burn through. This commonly happens when welding thin plates.
Solution:
5. Spatter
Spatter refers to molten metal splashing out during the welding process, leaving small particles around the weld. These spatters not only affect the appearance of the weld but also increase the post-welding cleaning workload.
Solution: