Deep Dive into OEM Metal Stamping in China
Table of Contents
Understanding OEM Metal Stamping
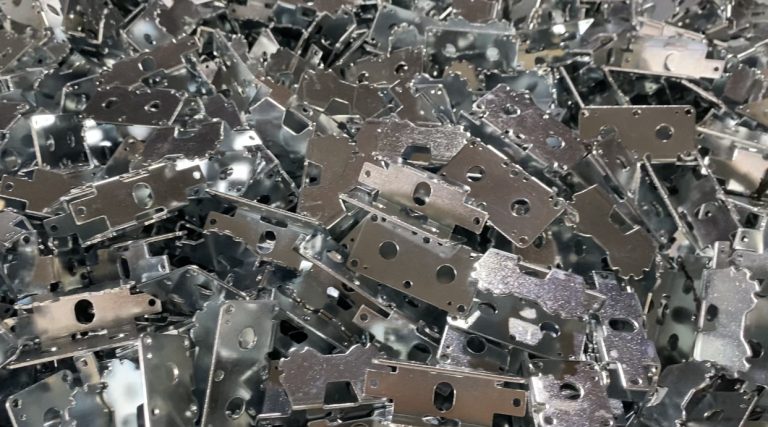
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) metal stamping refers to contract-based production of stamped metal components based on customer-supplied designs, drawings, or 3D models. The stamping process typically includes:
Why China? Technical Strengths in OEM Metal Stamping
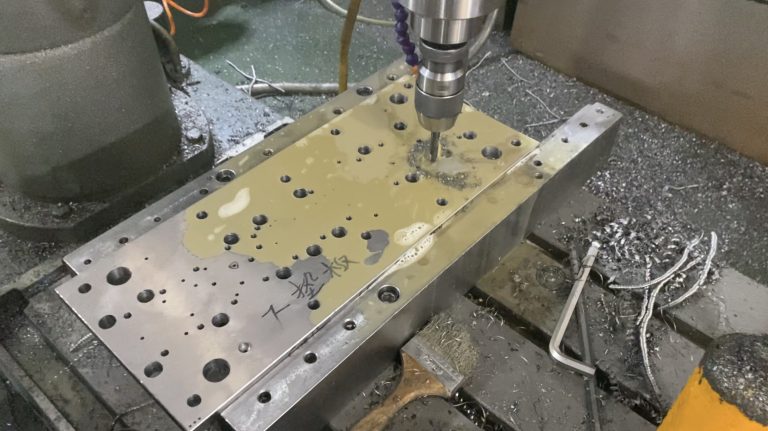
Tooling and Die Engineering Capabilities
Top-tier Chinese metal stamping suppliers invest heavily in in-house tool and die design, using CAD/CAM systems like SolidWorks, AutoForm, or UG NX. Progressive dies, transfer dies, and deep-draw tooling are commonly used depending on part complexity.
Tool steel selection (e.g., SKD11, DC53) and heat treatment processes are optimized for longevity and precision, especially for high-volume stamping.
Material Sourcing
Chinese OEMs are well-versed in international material standards (ASTM, JIS, DIN). Typical metals include:
Cold-rolled steel (SPCC, DC01)
Stainless steel (SUS304, 316)
Aluminum (5052, 6061)
Copper/brass alloys
Material traceability and certifications (RoHS, REACH, DFARS compliance) are often standard in exports.
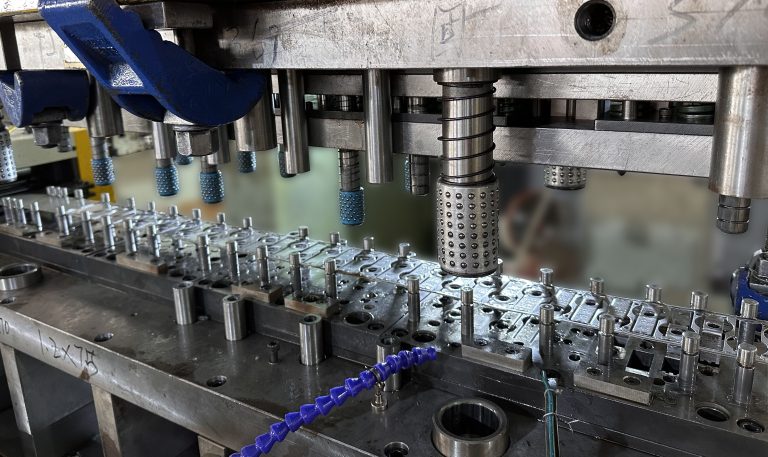
High-Precision Machinery
Modern stamping workshops in China run high-speed presses (from 25T to 800T), often from Japanese or German brands like AIDA, SEYI, or Schuler. For thin, tight-tolerance parts (±0.01 mm), servo-driven presses are used to maintain repeatability and tool protection.