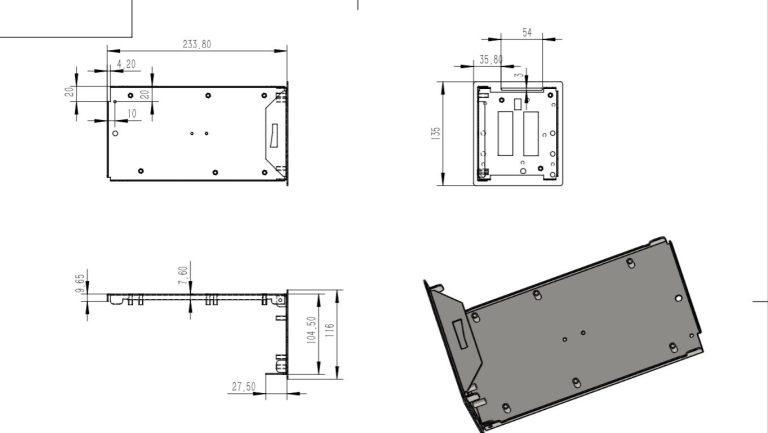
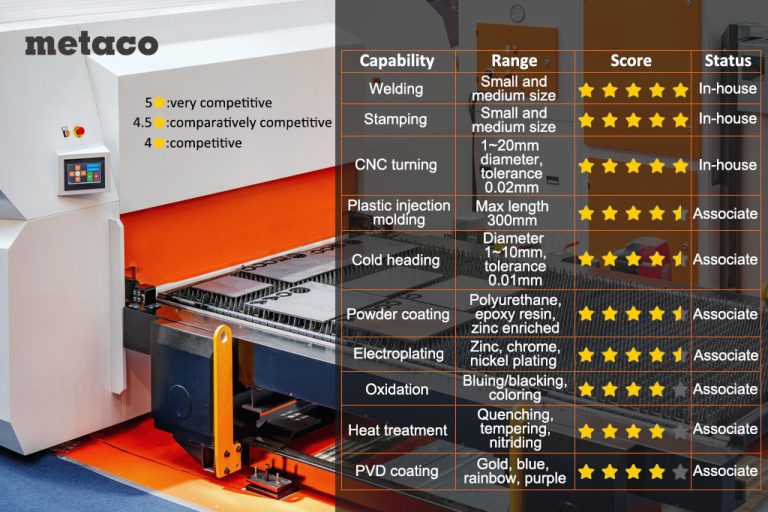
How to Quickly Evaluate the Process Capability of a Stamping Supplier
For stamping parts with complex structures or demanding tolerances, a supplier’s actual process capability directly impacts delivery risk. The following five criteria can be used for rapid, early-stage assessment of potential suppliers:
Table of Contents
1. In-House Tooling Development and Adjustment Capability
Why it matters: Tooling defines forming stability and dimensional control. Suppliers without in-house die-making struggle with response time during trials and production, leading to persistent quality issues.
How to assess:
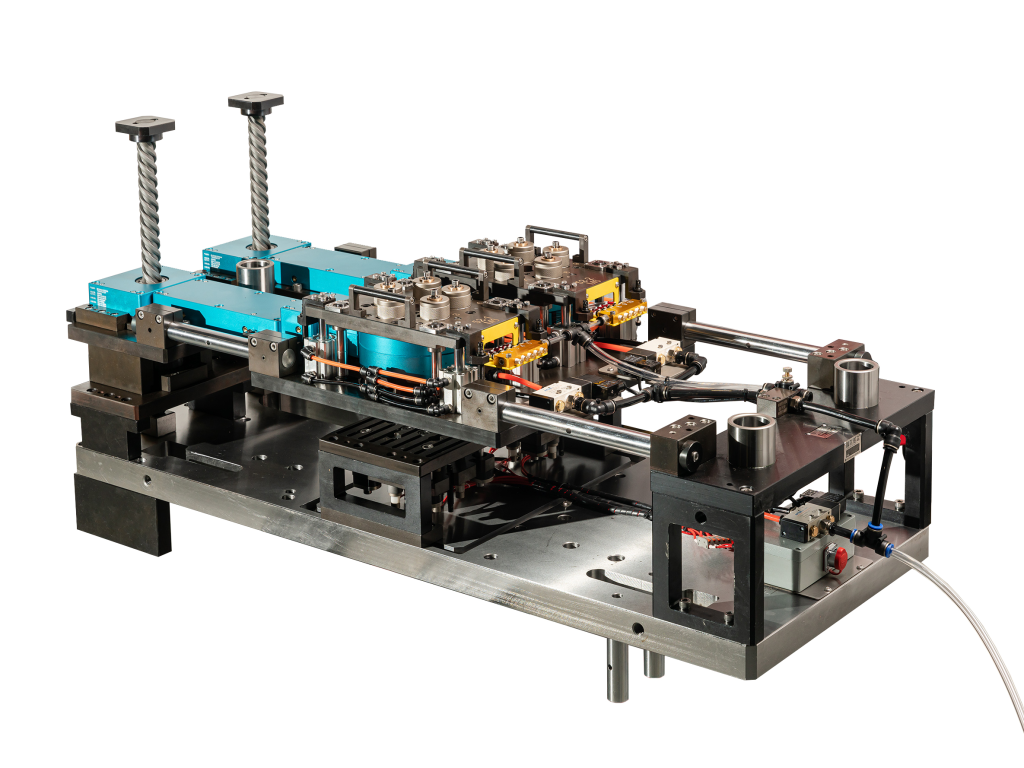
2. Equipment Configuration Matched to Product Requirements
Why it matters: Mismatched equipment (e.g., insufficient tonnage, lack of draw pads or servo control) increases the likelihood of defects such as cracking, distortion, or surface damage.
How to assess:
3. Process Parameter Monitoring and Traceability
Why it matters: Process fluctuations are inherent in stamping. Without parameter tracking and analysis, consistent quality cannot be maintained.
How to assess:
4. Material Control and Edge Forming Reliability
Why it matters: Material variability (e.g., reduced hole expansion ratio) often causes edge cracking or flange failure. Low-capability suppliers usually lack incoming material validation or batch-specific control.
How to assess:

5. Involvement in Customer Engineering Discussions
Why it matters: Competent suppliers actively engage in early-stage DFM reviews and suggest design optimizations. Those who don’t are typically just executors, not technical partners.
How to assess: