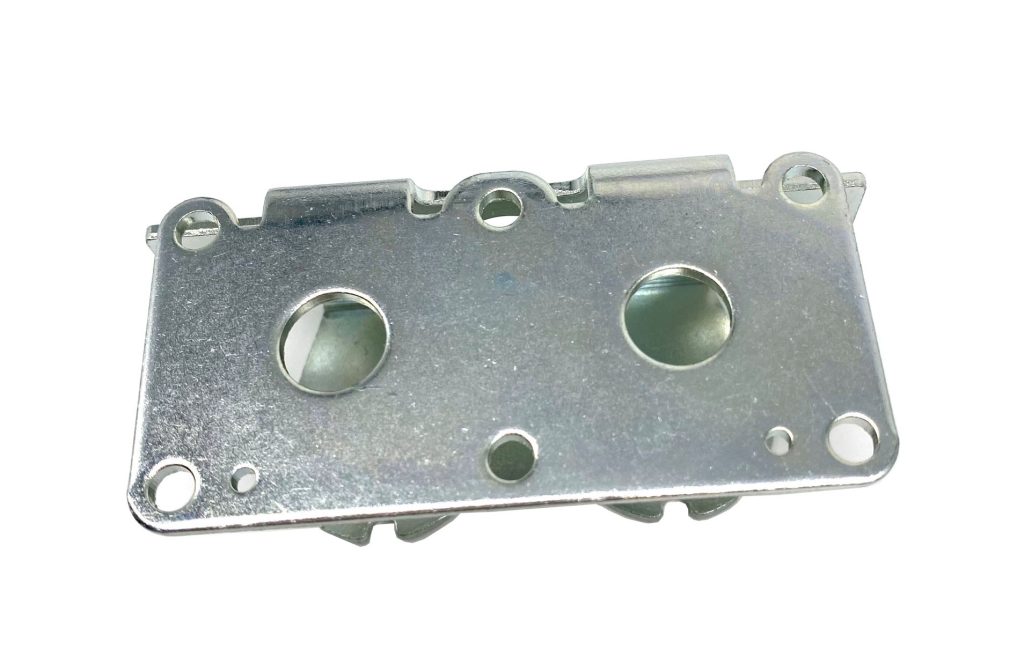
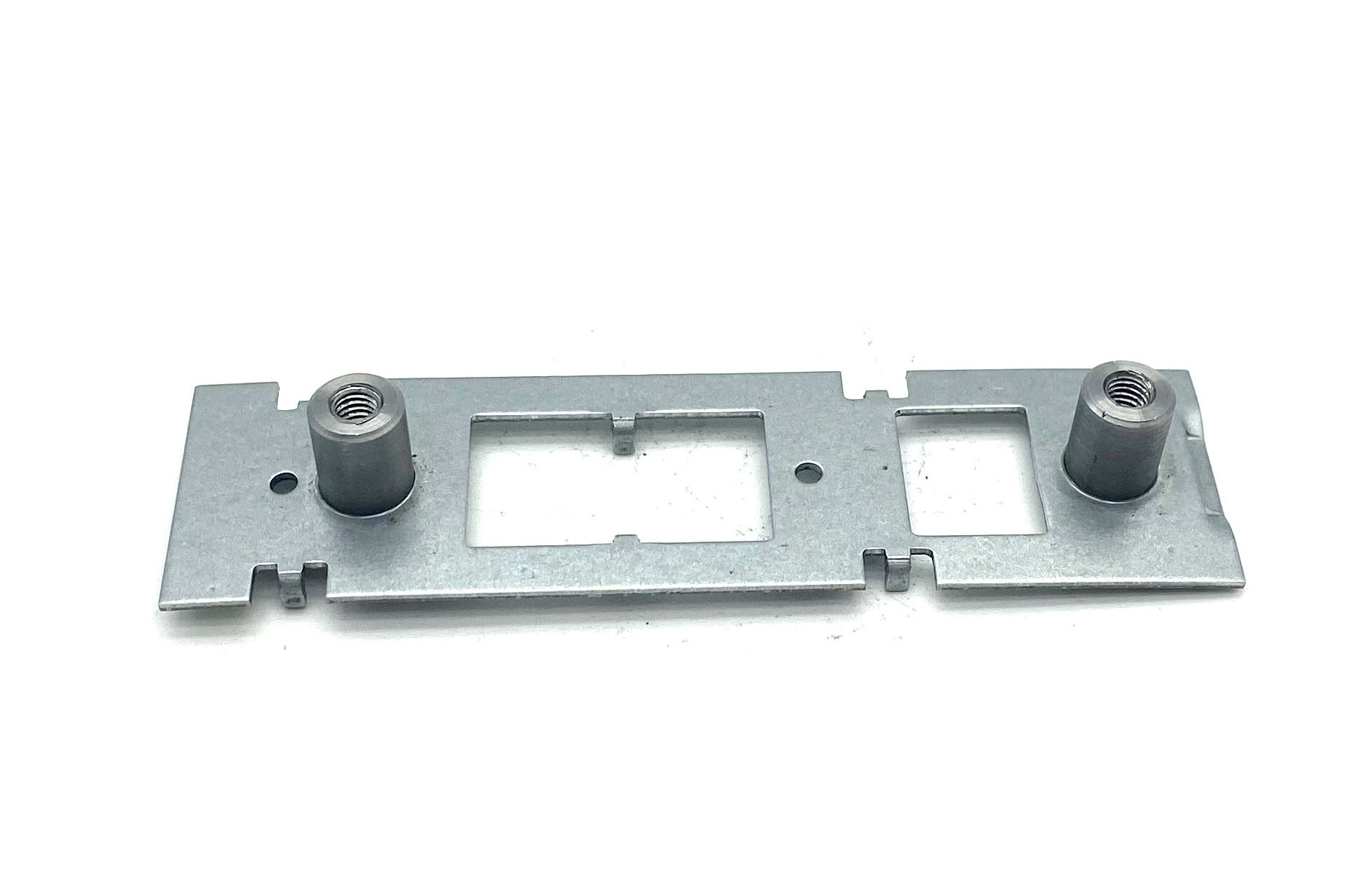
Metal Stamping China OEM
As a metal stamping China manufacturer, we offer one-stop stamping services to deliver high precision metal stamping parts. We got TS16949 certification, focus on production integrity and transparency.
Explore metaco services
parts secondary Operation
Explore metaco services
Delivery of stamped parts
Why source metal stamping parts from China?
Despite the trend of moving labor-intensive industries to other regions, China remains the first choice for metal stamping parts with higher technological value added. If you have a regular need for metal stamping parts, pursue high quality and cost efficiency, and tolerate up to one month’s ocean freight arrival time, then sourcing metal stamping parts from China is still the first choice.
Resource-Rich
China has rich resources of professional metal stamping tool and die design engineers, well trained press operators, wide range of metal stamping equipment.
Multi-Materials
Aluminum, copper, SPCC, SPHC, SECC, stainless steel and spring steel. China is a mainstream origin of these materials in the international market. To prepare the material for stamping in custom strips can be done immediately.
Secondary Operations
Various secondary operations including heat treatment, powder coating, zinc plating, nickel plating, oxidizing, blacking and overmolding are available at competitive costs.
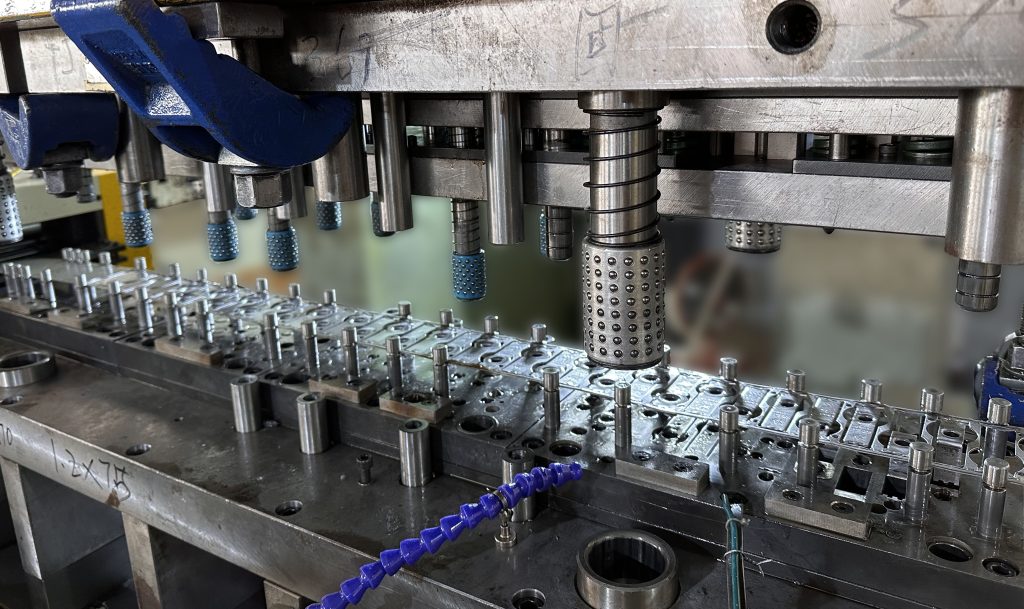
Our Metal Stamping Service
Fine Blanking
Bending
Punching
Coining
Curling
Flanging
Cutting
Progressive Die Stamping
Transfer Die Stamping
Deep Draw Stamping
Single Die Stamping
Compound Die Stamping


Why work with Metaco?
Philosophy of partnering
Dedicated team
Expertise and deep-in capability
comprehensive technical background
One-Stop In-House Services
With Metaco, you gain access to comprehensive in-house services that cover everything from design and manufacturing to post-processing. This integration of services streamlines production, reduces turnaround times, and cuts costs. Our versatile capabilities allow us to match your business growth, supporting you at every stage of your journey.
Customized Solutions
At Metaco, we understand the unique requirements of each project. We provide tailored metal stamping solutions designed to meet specific technical and business needs. Our team employs advanced technology and targeted strategies to ensure each solution is precise and meets client specifications.
Efficient, High-Quality Production
We commit to maintaining high standards of quality while delivering efficient production. Our quality control measures, including TS16949 certification, ensure consistent in every batch. Our skilled production team manages to deliver products promptly without compromising quality.
Markets we serve
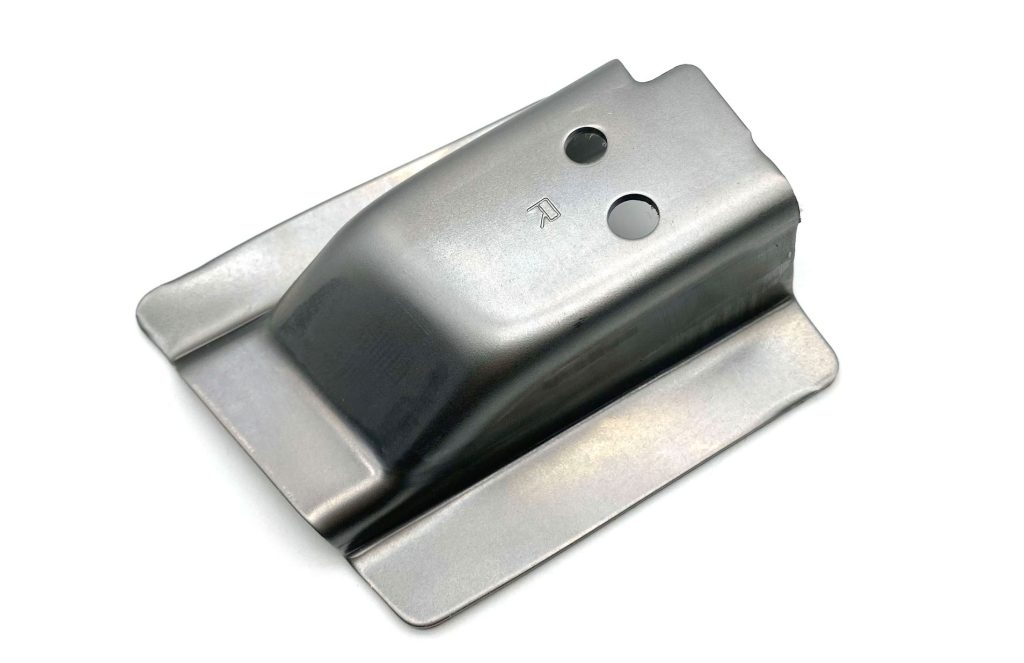
Precision Coining Part
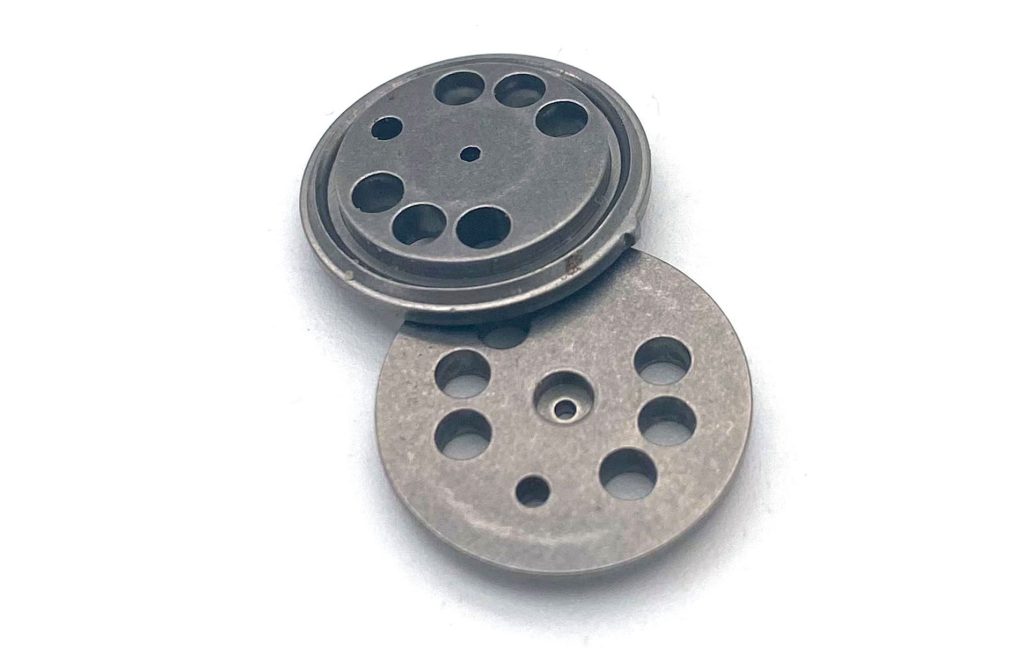

Photovoltaic
- Brake Components
- Battery Trays
- Compression Limiters
- Crush Bushings
- Floor Panels
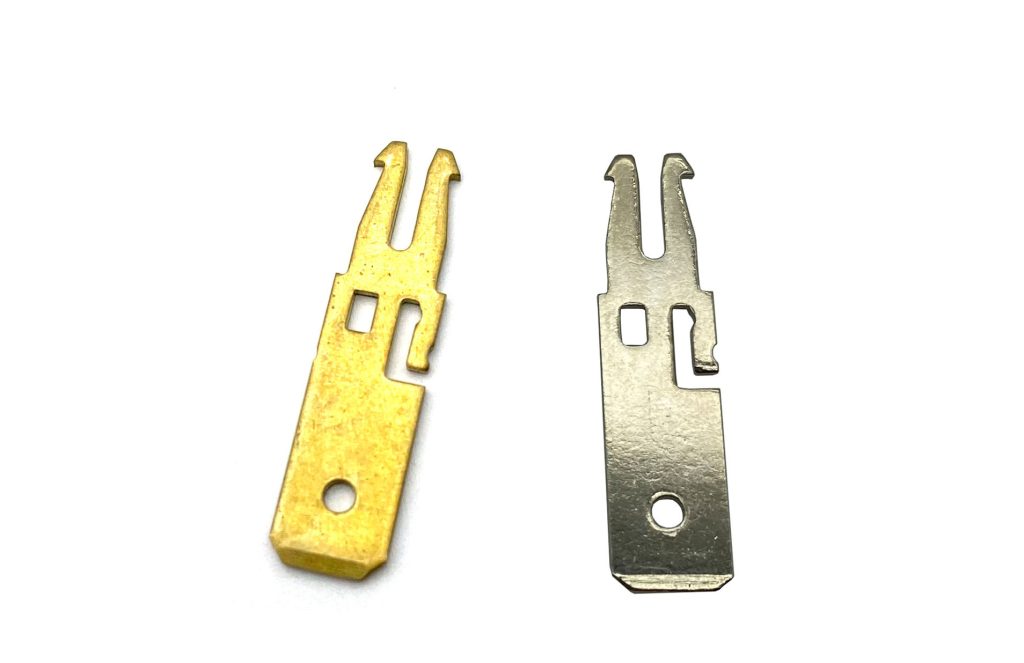
- Terminals
- Contacts
- Connectors
- Wire and Cable Connectors
- Press-fit Pins
- Retainer Clips
- Hose Clamps
- Fasteners
- Housings
- Rolled Bushings
- Shields
- Inserts
- Cylinder Head Gaskets
- EV Charging Components
- Radiator Frame Assemblies